Volatility Arbitrage Strategies
Volatility arbitrage strategies refer to combinations of different options and other derivatives (such as futures) to arbitrage based on expected volatility changes. These strategies typically exploit differences between implied volatility and realized volatility in the market, or construct strategic combinations based on judgments about current volatility.
traddle Strategy
Definition:
- Straddle strategy involves simultaneously buying a call option and a put option on the same underlying asset with the same strike price and expiration date.
- Objective: Profit from significant price movements of the underlying asset, regardless of direction (up or down).
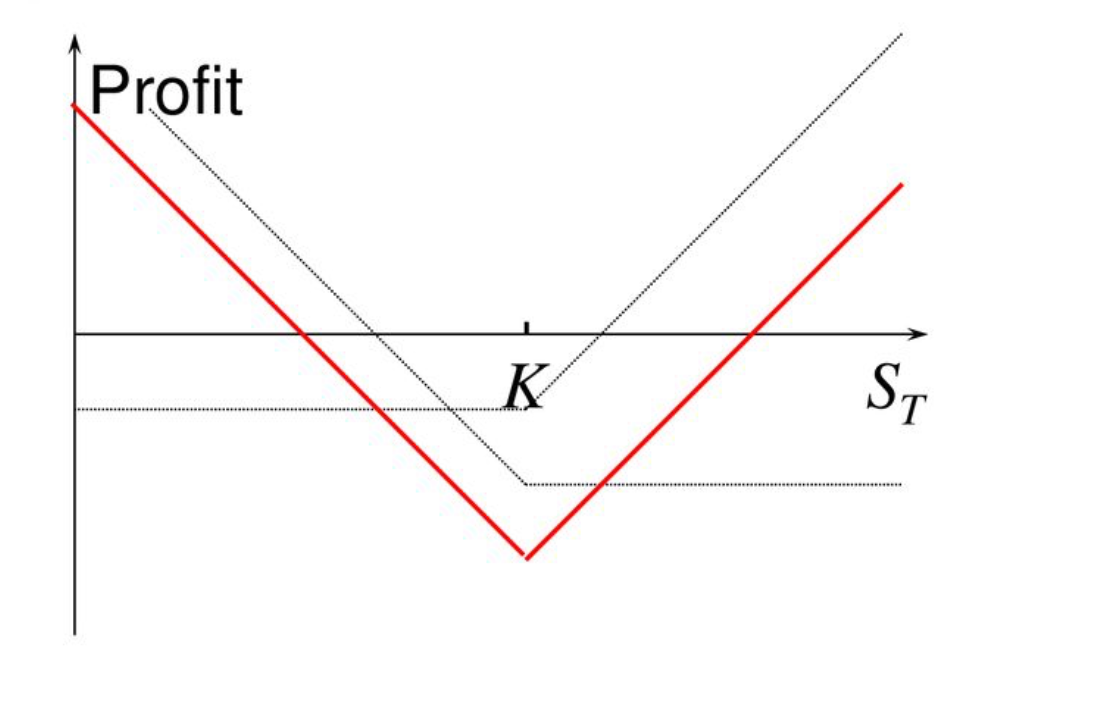
Strategy Summary:
Bidirectional Profit: If price moves significantly up or down, one of the purchased options will profit enough to cover the loss of the other.
High Risk: Options require sufficiently large price movements to offset the premium cost. If price changes are small, options will expire worthless, causing significant losses.
High Cost: Since both types of options are purchased simultaneously, the initial cost (premium) of straddles is typically high.
Straddle Strategy Application
Assume that BTC current price is $100,000. You expect BTC to have significant volatility but cannot determine whether it will rise or fall, so you decide to use a straddle strategy:
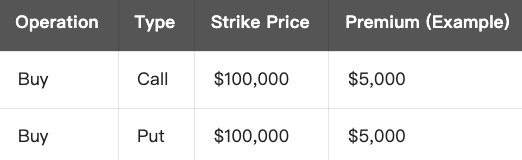
Net Expense :
- Total Cost = $5,000 (Call Premium) + $5,000 (Put Premium) = $10,000
PnL at Expiration:
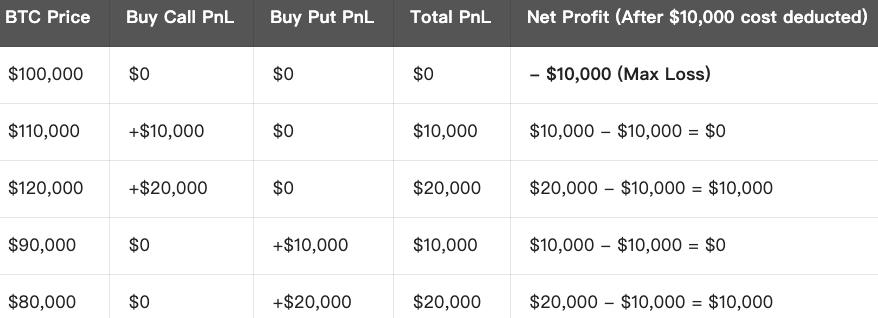
Strategy Summary:
Max Loss: When price remains unchanged or volatility is insufficient, max loss equals total premium paid ($10,000).
Max Profit: There is no upper limit, as long as the price fluctuation is large enough, the profit will continue to increase.
Breakeven point: The price movement must exceed the total premium, which is **$100,000 + $10,000 = $110,000** or $100,000 - $10,000 = $90,000.
Application Scenario:
- Straddle strategies are typically suitable when expecting significant volatility over a period but are uncertain about direction. For example, before the release of financial reports, government announcements, or major events.
Conclusion:
Straddle strategy is suitable when both upward and downward movements are possible, profiting from significant underlying asset volatility, but requires sufficient volatility to cover option costs.
Strangle Strategy
- Strangle strategy is suitable when expecting significant underlying asset volatility but uncertain about price direction. This strategy is similar to straddles but uses different strike prices, typically requiring lower premium outlay.
- The main purpose is to profit from significant price movements regardless of direction.
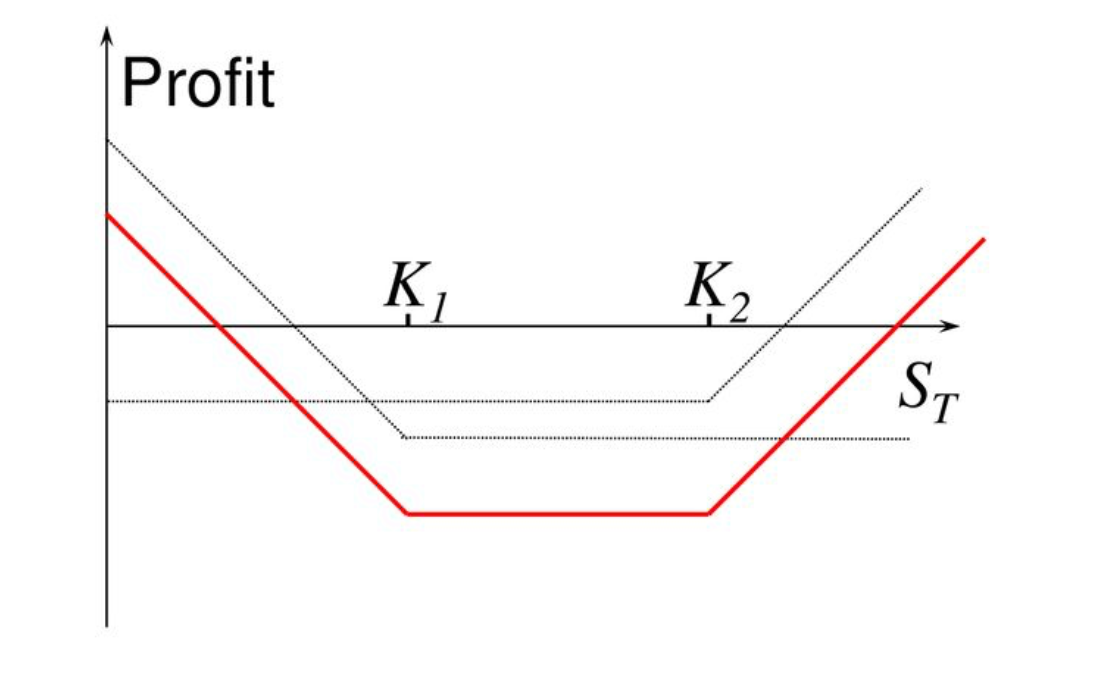
Difference from Straddle:
- Straddle: Buy call and put options at the same strike price.
- Strangle: Buy call and put options at different strike prices, usually with some distance between strikes, resulting in lower total cost.
Strangle Strategy Application
Assume that BTC current price is $100,000. You expect BTC to have significant volatility but cannot determine whether it will rise or fall, so you decide to use a strangle strategy:
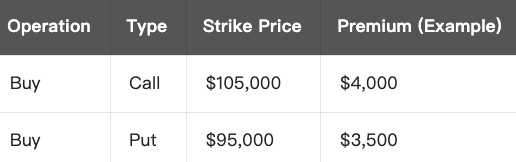
Total Cost:
- Total Cost = $4,000 (Call premium) + $3,500 (Put premium) = $7,500
PnL at Expiration:
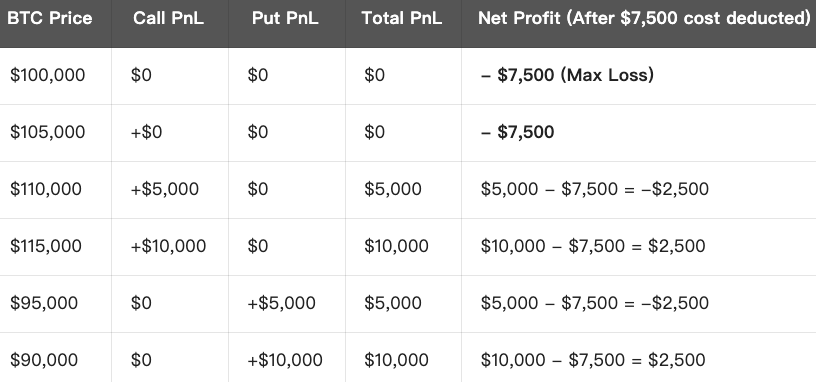
Strategy Summary:
Max Loss: When market price stays between the two strike prices, max loss equals total premium paid ($7,500).
Max Profit: There is no upper limit, as long as the price fluctuation is large enough, profit will increase with upward or downward price movement.
Breakeven Point: Price movement must exceed total option cost:
- Upward Breakeven Point = Strike Price (Call) + Total Premium = $105,000 + $7,500 = $112,500
- Downward Breakeven Point = Strike Price (Put) - Total Premium = $95,000 - $7,500 = $87,500
Application Scenario:
Strangle strategy is suitable when expecting significant volatility in the underlying asset but the direction of the move is uncertain.
Examples: upcoming financial reports, policy announcements, major market events, etc.
- The main advantage is lower premium outlay compared to Straddle, with lower risk but requiring larger price movements to profit.
Conclusion:
Strangle is a strategy that capitalizes on significant volatility in underlying assets through low-cost purchase of calls and puts at different strikes, providing a low-risk way to profit from large market swings.
Short Strangle Strategy
Definition:
- Short Strangle involves selling a call option and a put option on the same underlying asset with different strike prices and the same expiration date.
- This strategy is suitable when expecting no significant market volatility, with the underlying price remaining within a certain range.
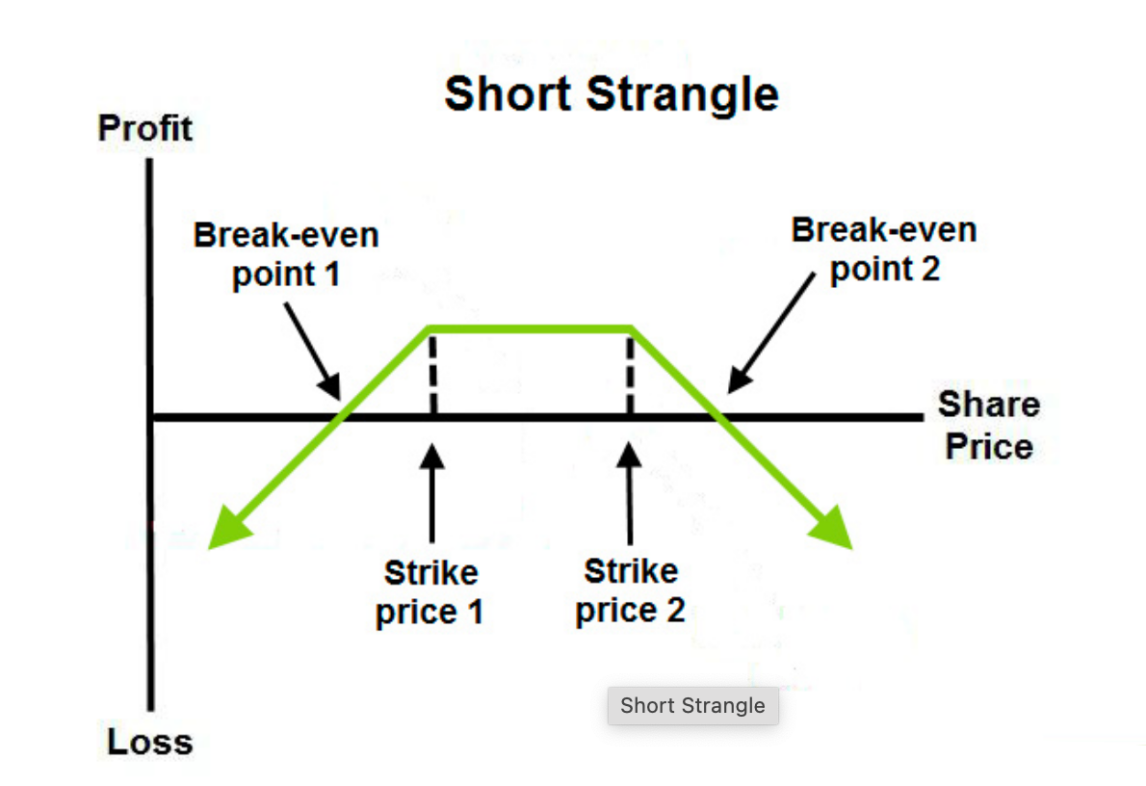
Goal:
- Profit by collecting premiums from both options while bearing risk if price volatility is excessive.
- If price stays between the sold options’ strike prices, the seller retains all premium income.
Short Strangle Application
Assume that BTC current price is $100,000, you expect BTC price will not fluctuate significantly over the next few days, so you decide to implement a short strangle strategy:
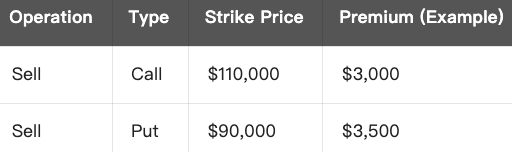
Total Income (Premium Income):
- Total Cost = $3,000 (Call Premium Received) + $3,500 (Put Premium Received) = $6,500
PnL at Expiration:
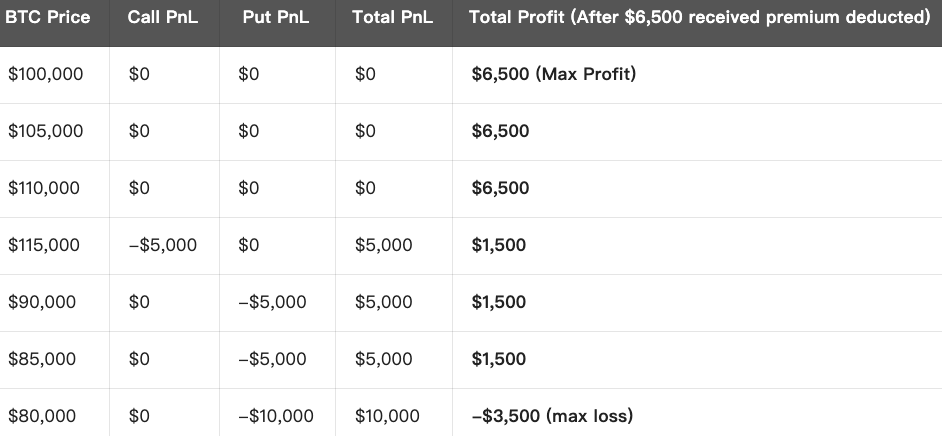
Strategy Summary:
Max Profit: When underlying asset’s price fluctuates between the two strike prices, premium income from selling options is the max profit ($6,500).
Max Loss: If market price volatility is excessive, exceeding the sold options’ strike prices, seller’s loss increases infinitely. Maximum loss is strike spread ($110,000 - $90,000 = $20,000) minus total income ($6,500) = $13,500.
Breakeven Point: The breakeven point is the two strike prices plus or minus the total income:
- Upward Breakeven Point = $110,000 + $6,500 = $116,500
- Downward Breakeven Point = $90,000 - $6,500 = $83,500
Application Scenario:
- Short Strangle is suitable when markets are unlikely to experience significant volatility. For example, expecting range-bound markets or when upcoming events (the release of financial reports, economic data) fail to trigger major movements.
- The strategy’s maximum risk occurs when underlying price moves significantly beyond the sold options’ strike prices.
Conclusion:
Short Strangle is suitable when expecting stable market prices, earning option premiums. Please beware of potentially huge losses during violent price movements.





